PROCESS CONTROL SYSTEM – TYPES OF PROCESS
Type of
processes carried out in modern manufacturing industries can be grouped into 3
general areas in term of the kind of operation that takes place:
a.
Continuous process
Is one in which raw materials enter one end
of the system and the finished product comes out the other end of the system.
The picture shows a continuous process
engine assembly line. Engine blocks are fed into one end of the system and
completed engines exit at the other hand. In the continuous processes, the
product material is subjected to different treatment as it flows through the
process (in this case, assembly, adjustment, and inspection). Auto assembly
involves the use of automated machines or robots. At each station, parts are
supplied as needed.
b.
Batch production
In batch processing these is no flow of
product material from one section of the process to another. Instead, asset
amount of each of the input to the processes is received in a batch and then
some operation performed on the batch to produce a finished product or an
intermediate product that need further processing. Each batch of the product
may different.
c.
Individual products production
The individual product production process
is the most common of all processing system. A series of operation produces a
useful output product. The item that produced maybe required to be bent,
drilled, welded, and so on at different step in the process. The workpiece is
normally a discrete part that must be handled on an individual basis.
The control of machines or processes can be
divided into the following categories:
·
Electromechanical control
·
Hardwired electronic control
·
Programmable Hardwired electronic control
·
Programmable logic control (PLC)
·
Computer control
Possible control configuration include:
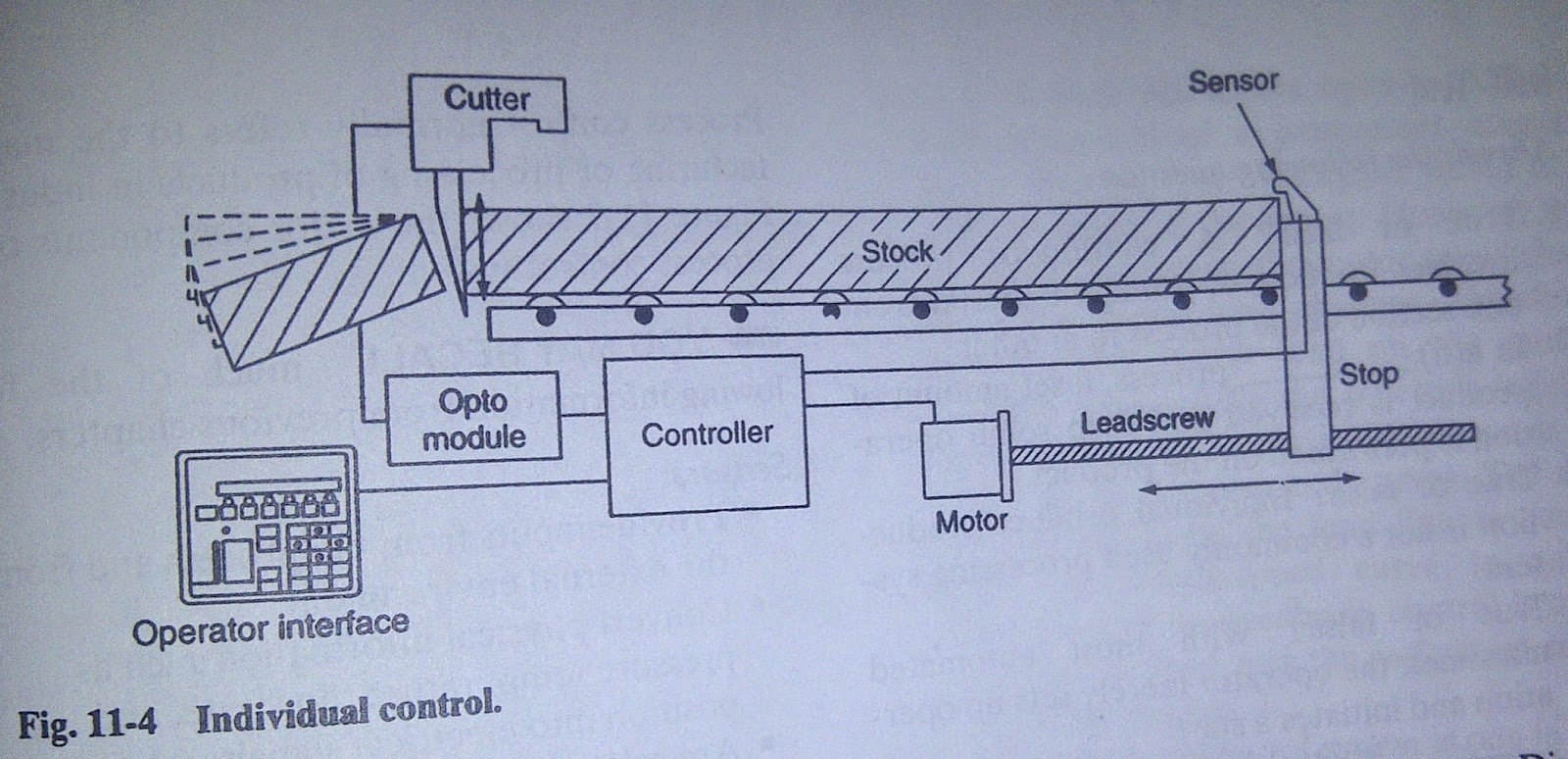
a.
Individual control (is used to control single
machine, doesn’t normally required communication with other controller)
b.
Centralized control (is used when several
machines or processes are controlled by one central controller. This control
layout utilizes a single large control system to control many diverse
manufacturing processes and operation. Each individual step in the
manufacturing process is handled by a central control system controller. No
exchange of controller status or data is sent to other controller)
c.
Distributed control (differs from centralized
system in that each machine is handled by a dedicated control system. Each
dedicated control is totally independent and could be removed from the overall
control scheme if it were not for the manufacturing function perform.
Distributive control involved two or more computer communicating with each
other to accomplish the complete control task)
Petruzella, Frank. 1996. Industrial Electronics. Mc-Graw Hill. Singapore





Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar